Set up aerial survey control points
This article mainly describes how to set up control points correctly.
Overview
Control Point(Ground control point):It is mainly used to correct the three-dimensional space position error caused by various factors; the position accuracy of the control point will affect the accuracy of the results.
Check point:Measurement points used to calculate errors in aerial survey results
Control Point(Ground control point)
Use control points to correct the target three-dimensional space error caused by various factors; if you use rtk or ppk and do not require high accuracy, you can not lay out control points; the more control points, the more accurate the output, the better the results.
C-RTK2 PPK can reduce the control points by more than 80%. For common aerial survey areas and accuracy requirements, it is only necessary to ensure that there are 1 to 2 control points per square kilometer. Control points are not required if position errors of 5cm and more are allowed. The final effect is subject to the actual situation.
How to lay out control points?
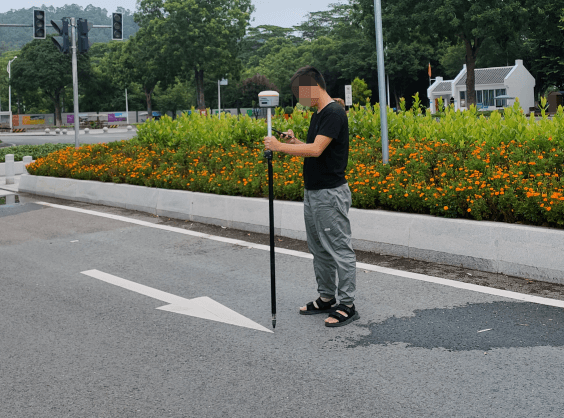
- Start the RTK measuring instrument and connect the CORS account
- Hold the RTK measuring instrument and make sure that the pole is perpendicular to the horizontal plane (the bubble of the spirit level is in the center)
- Enter the point measurement mode and wait to enter the fixed solution; when both HRMS and VRMS are greater than 0.02, click the point measurement icon to complete the measurement
- After the control point collection is completed, take at least 3 environmental photos of the control point;
- Create separate folders for control points, check points and corresponding photos, and place them in separate folders; save the .csv files of all control points and checkpoints outside the folder

It is necessary to ensure the consistency of the image control points, check points and the result coordinate system.
Rules for laying control points
Regular rectangle
At least 4 control points (four corners) are arranged at the edge of the survey area in small area, and one point is deployed in the middle area; control points are added in rules for large area.
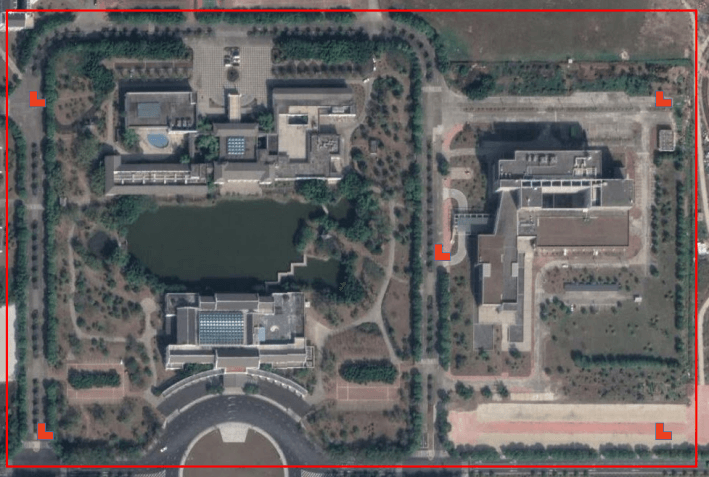
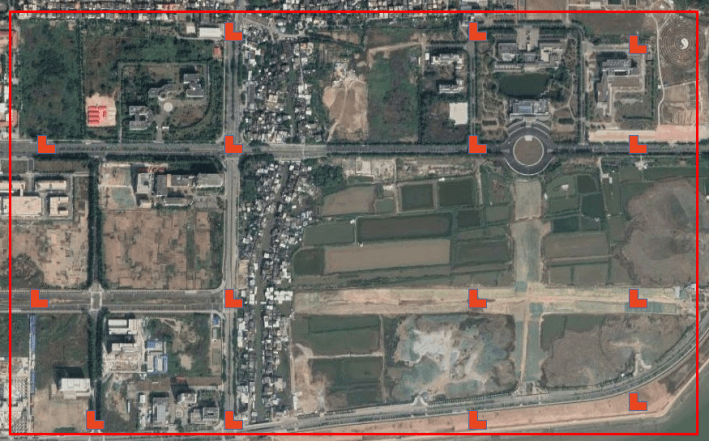
Irregular shape
In most cases, our aerial survey area is not a regular area. At this time, we need to comprehensively deploy the topography, convenience and other factors of the points to be deployed, and try to ensure that the deployed control points can evenly cover the survey area.
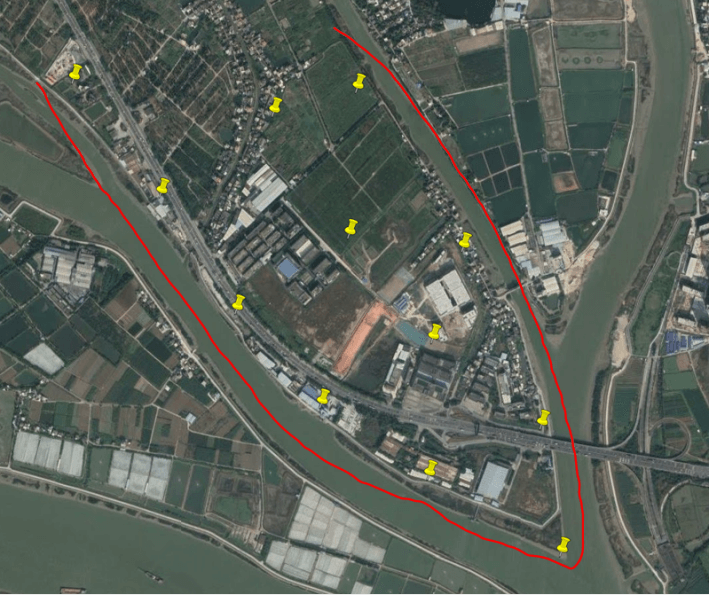
belt Aerial survey area
For banded areas such as rivers and highways: "Z" type control points are generally used.
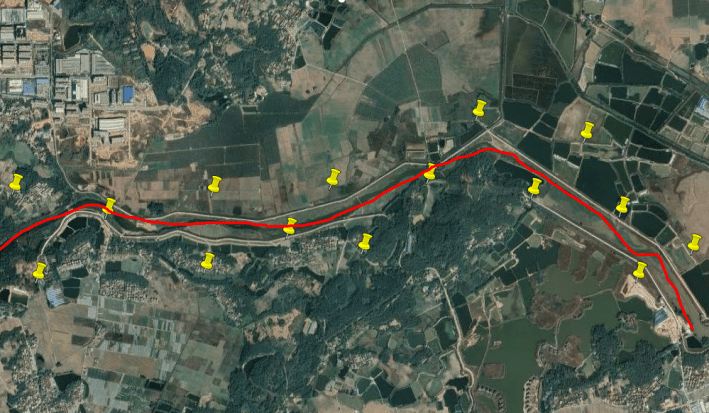
Other situations that affect the layout of control points
- Camera pixel size: camera pixel size; the higher the pixel, the smaller the pixel density
- Flight altitude: The lower the flight altitude, the greater the density of control points.
- Equipment type: Aircraft with PPK (Post Differential System) have more than 80% fewer control points than those without PPK
Selection condition
- The general rule for selecting points is "Easy to find, easy to identify, good field of view, clear edges and corners"
- The target of the control point should be flat, clear, without shadows, with good field of view conditions, which can be found from all angles, and it is not recommended to lay control points next to trees and buildings.
- Control points need to be selected as sharp markers with clear edges and corners
- Manual control point marking paint width>30CM, markers should be larger than 70CM
- The control point identification should be clearly different from the surrounding color
Control point sign
Make control point signs, use a right-angle mold to spray, or use a special sign for aerial survey; the sign is larger than 50cm, with a logo and a clear identification number, and the logo must be at a right angle; the height of the font is greater than 30cm.


Other control point signs
In the urban environment, if there is no condition to make like the control point mark, the road indicating arrow can also be used as the control point signs